<TODO>: Insert description text here... And don't forget to add keyword for this topic
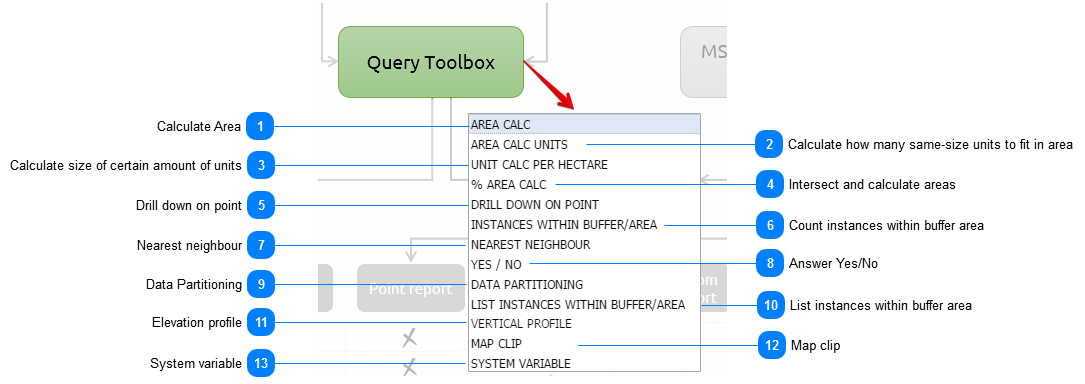
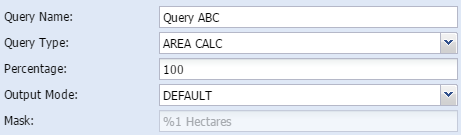
 Calculate AreaArea calc is a simple calculation of the total area of the study area in hectares.
In addition the user can either calc the total area of the study area or a portion of the area. In the parameters field the user can type in what percentage of the site the area should be calculated on.
|
When to use:
When the area of a land parcel needs to be calculated and reported on.
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Percentage - The user can decide how big a portion of the area should be displayed
-
-
Mask - shows how the output are constructed
|
|
|
|
|
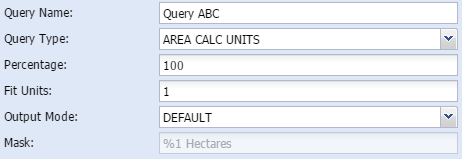
 Calculate how many same-size units to fit in areaThis method assist the user to calculate the average size of parts if it is to be split in a certain amount of parts. Yet again, the user can do the calculation on only a certain percentage of the total study area as well.
|
When to use:
To calculate the average size of the area if it is to be split in a certain amount of parts.
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Percentage - The user can decide how big a portion of the area should be displayed
-
Fit units - user type in how many units needs to be fit in the area
-
-
Mask - shows how the output are constructed
|
|
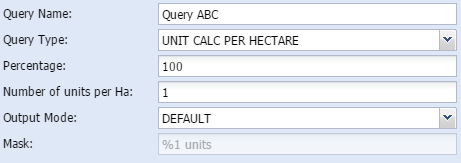
 Calculate size of certain amount of unitsWith this method, the user can calculate how many units will fit in the study area if it is to be of a certain size. The user can do the calculation on only a certain percentage of the total study area or the full area.
|
When to use:
To calculate how many units will fit in the study area if it is to be split by a certain unit per hectare ratio.
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Percentage - The user can decide how big a portion of the area should be displayed
-
Number of units per Ha - user type in how many units per hectare needs to be fit in the area
-
-
Mask - shows how the output are constructed
|
|
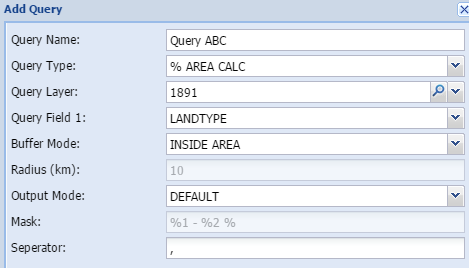
 Intersect and calculate areasThe percentage area calculation tool intersects the study area with a chosen theme and calculate the percentage of each part of the chosen theme which intersects the study area.
|
When to use:
-
Percentage of different land use in the study area. -
The same as above for any other relevant polygon layer like geology, waterbodies, wetlands etc.
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
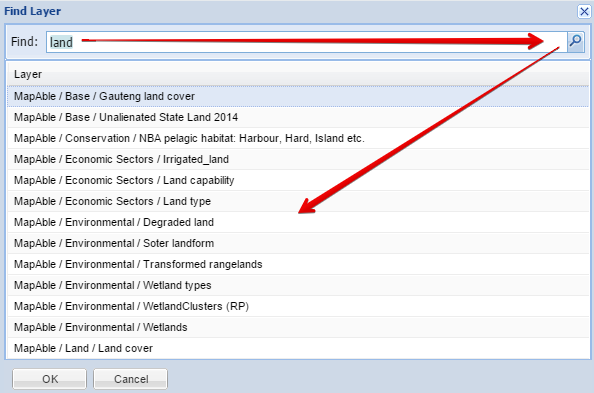
Query layer - Select the layer to be queried in the spatial database
-
Query field 1- Select the column in the attribute field of the queried layer
-
-
Radius (km) - add the buffer distance in km
-
-
Mask - shows how the output are constructed
-
|
|
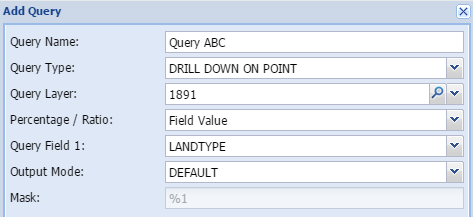
 Drill down on pointDrill down on point is a simple overlay analysis based on the point of the centroid of the study area. If a polygon is used as the study area, the tool calculates the centroid of the polygon and establish the value of the specified layer at that specific point. It then reports on it.
|
When to use:
Whenever the user want to establish in which broader area the study area falls. When the study area is very large, it is not advisable to use this with detailed layers like land cover or environmental constraints etc. It can be typically used to establish the administrative boundaries of the area (e.g. Municipality, ward, province, suburb)
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Query layer - Select the layer to be queried in the spatial database
-
-
Query field 1- Select the column in the attribute field of the queried layer
-
-
Mask - shows how the output are constructed
|
|
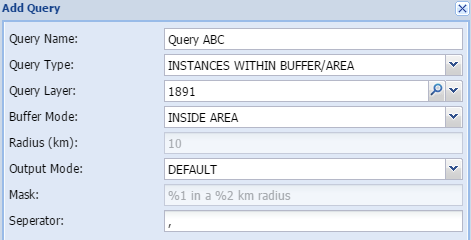
 Count instances within buffer areaThis tool calculates the number of instances of another layer that can be found within a specified distance from the study area.
|
When to use:
Calculating the incidences of any type of layer within distance. Typically schools, hospitals, heritage sites, informal settlement, housing workspaces etc.
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Query layer - Select the layer to be queried in the spatial database
-
-
Radius (km) - add the buffer distance in km
-
-
Mask - shows how the output are constructed
-
|
|
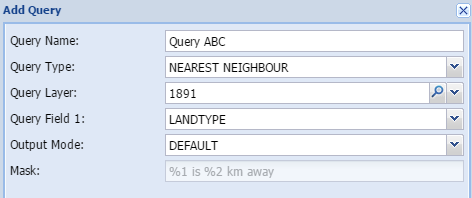
 Nearest neighbourThe nearest neighbour calculation will determine the nearest instance of the specified layer. It will report on it by indicating the distance in kilometre and indicating the name
|
When to use:
Typically used for public facilities like schools, hospitals, public transport stations.
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Query layer - Select the layer to be queried in the spatial database
-
Query field 1- Select the column in the attribute field of the queried layer
-
-
Mask - shows how the output are constructed
|
|
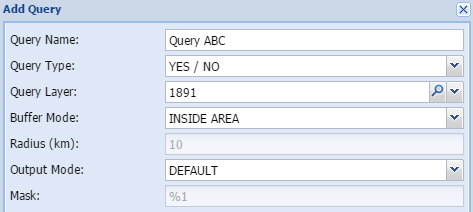
 Answer Yes/NoThe YES/NO method does a quick check by means of an intersection, and simply reports on the presence of a specific entity that are present on the property. The answer is either YES or NO.
|
When to use:
Normally you would use this when detailed information on an entity is either not available or not necessary. This will just raise a red flag if a specific entity occurs on the site.
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Query layer - Select the layer to be queried in the spatial database
-
-
Radius (km) - add the buffer distance in km
-
-
Mask - shows how the output are constructed
|
|
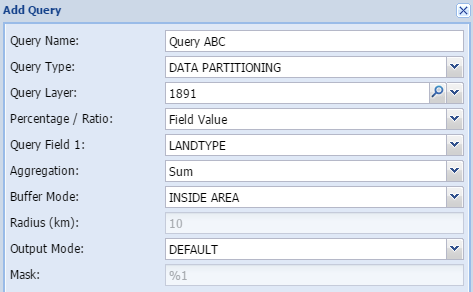
 Data PartitioningData partitioning can be used to calculate demographic or other data proportionately based on another polygon theme. For example, people often need information on census demographics for areas that are not coincident with the census boundaries themselves, things like catchment areas or service areas. This tool makes that process easy. The proportions are based on the area of the intersecting themes.
|
The aggregation function has the following options:
When to use:
Demographics, census statistics.
|
|
|
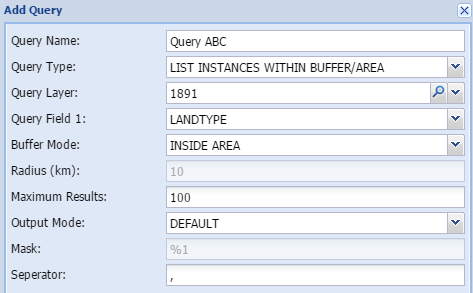
 List instances within buffer areaThis tool does exactly the same as the Instances within buffer zone, except that it does not count them but list them. This is very handy if you need to know the names of the objects you are studying.
|
When to use:
Listing the incidences of any type of layer within a specific distance. Typically schools, hospitals, heritage sites, informal settlement, housing projects etc.
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Query layer - Select the layer to be queried in the spatial database
-
Query field 1- Select the column in the attribute field of the queried layer
-
-
Radius (km) - add the buffer distance in kilometer
-
Maximum results - maximum number of results in the case of very detailed layers
-
-
Mask - shows how the output are constructed
-
|
|
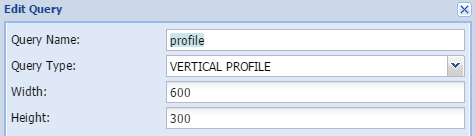
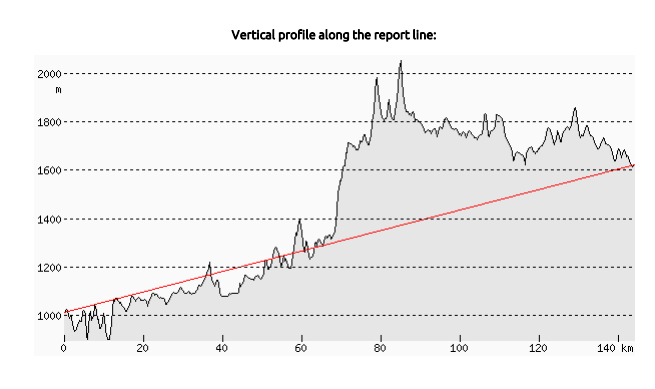
 Elevation profileThe user can view a graph of the elevations of a particular path through the Elevation Profile profile tool. This function is only applicable if a line is chosen as the study area. The result is given in km distance and meter in height.
|
The result will typically look like this:
When to use:
When the elevation profile of a road or any other route needs to be shown in a graphic format.
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Width - Width of the graphic in pixels
-
Height - Height of the graphic in pixels
|
|
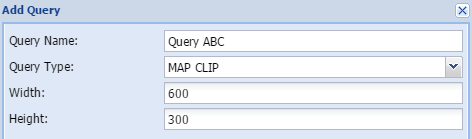
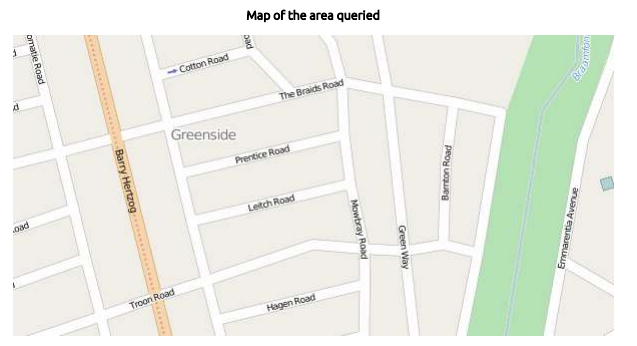
 Map clipA clip of the study area can be added to the report.
|
The result will typically look like this:
When to use:
When an overview map of the study area is required
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Width - Width of the graphic in pixels
-
Height - Height of the graphic in pixels
|
|
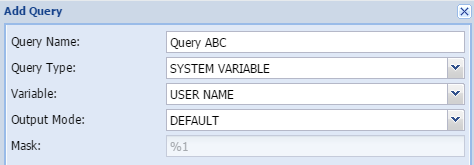
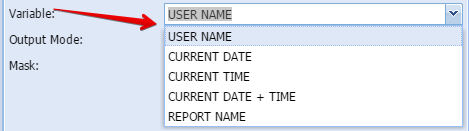
 System variableAdditional variables can be added to assist with administration and versioning of reports
|
The result will typically look like this:
When to use:
Mostly for administrative purposes to keep record of authors and versioning of maps.
|
-
Query name - The user gives the query a short, unique and descriptive name.
-
Variable - Type of variable to add (see below)
-
-
Mask - shows how the output are constructed
-
|
|
|