Data Fusion
Background on Data Fusion
Data fusion is the process of integration of multiple data and knowledge representing the same real-world object into a consistent, accurate, and useful representation. Data fusion processes are often categorized as low, intermediate or high, depending on the processing stage at which fusion takes place. Low level data fusion combines several sources of raw data to produce new raw data. The expectation is that fused data is more informative and synthetic than the original inputs.
In the Geospatial (GIS) domain, data fusion is often synonymous with data integration. In these applications, there is often a need to combine diverse data sets into a unified (fused) data set which includes all of the data points and time steps from the input data sets. The fused data set is different from a simple combined superset in that the points in the fused data set contain attributes and metadata which might not have been included for these points in the original data set.
MapAble Data Fusion processes
MapAble allows data fusion in several different ways. The first is done in the TABLE mode and the second in the MAP mode. The Data Fusion function in the MAP mode is primarily focused on data extraction through an analysis and query builder with the outputs presented in a report format. These results in the MAP mode are of a non-permanent nature and cannot be used for further analysis or fusion. The TABLE mode allows the user to add new fields and do further analysis and fusion either with the specific layer's attributes or any other layer in the spatial database. The result of the data fusion process in the TABLE mode is permanent and can be used in any of the other mapping, analysis and reporting processes.
|
|
Please note:
|
This section will give an overview of the Data Fusion processes in the TABLE mode. The following is a diagrammatic view of these processes:
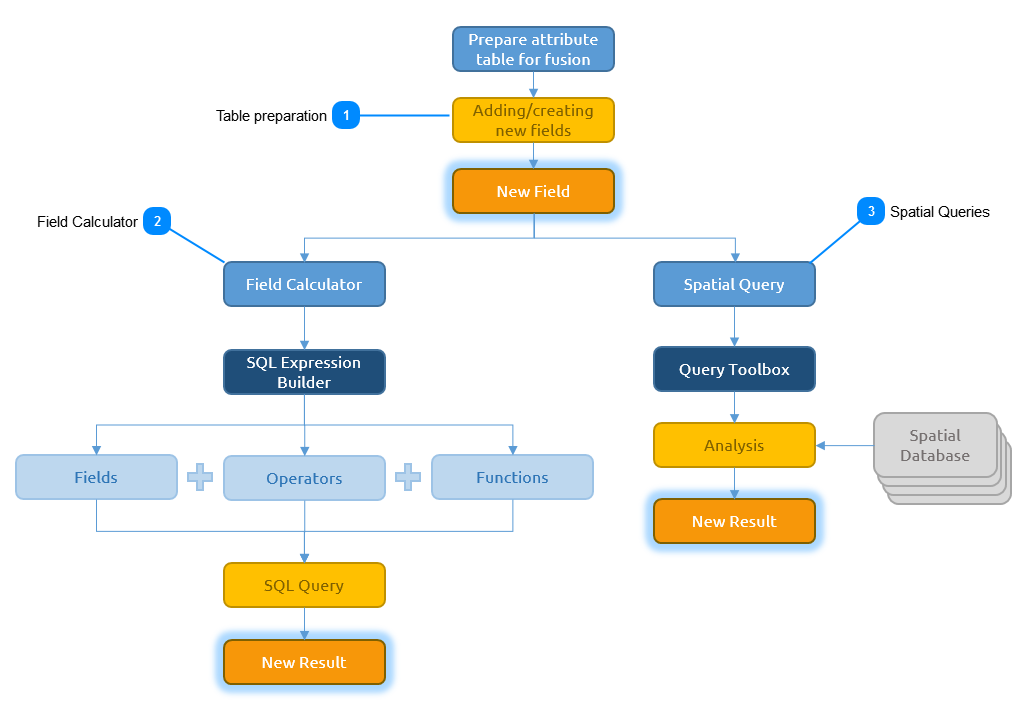
 Before the user can do any type of data fusion, an appropriate field in the attribute table needs to be selected or created. When an analysis needs to be done on an existing field, the user can simply select the field in the Table Mode. When an data fusion for a new value needs to be done, the user will need to create a new field in the attribute table. The following section explains how to create a new field in the table
|
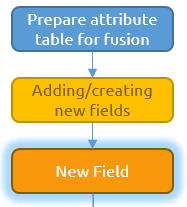
 The Field Calculator is used for copying fields, concatenating (i.e., combining) strings, performing most mathematical calculations, and entering raw data. The Field Calculator can be used for conditional reclassification, complex mathematical calculations, and extracting geometric and geographic information. The following section explains how to use the field calculator to add new data in the attribute table.
|
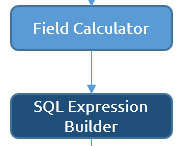
 Spatial analysis is the process of examining the locations, attributes, and relationships of features in spatial data through overlay and other analytical techniques in order to address a question or gain useful knowledge. Spatial analysis extracts or creates new information from spatial data. The following section will explain how to create new data by using the MapAble Spatial Analysis Toolbox.
|
